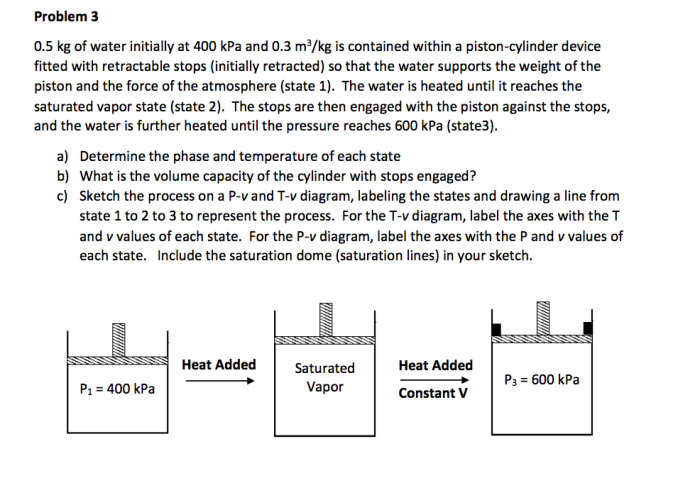
A closed rigid tank whose volume is 1.5 – A closed rigid tank with a volume of 1.5 cubic units plays a crucial role in various engineering applications. Its fixed volume and ability to withstand high pressures make it an essential component in systems involving fluid storage, transportation, and processing.
Understanding the properties of fluids within such tanks and the thermodynamic processes that occur is essential for optimizing their performance and ensuring safe operation.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate details of closed rigid tanks, exploring their design considerations, fluid properties, thermodynamic processes, and practical applications. By examining real-world case studies, we gain valuable insights into the effectiveness and limitations of these tanks, ultimately enabling engineers to make informed decisions in their design and utilization.
Closed Rigid Tank
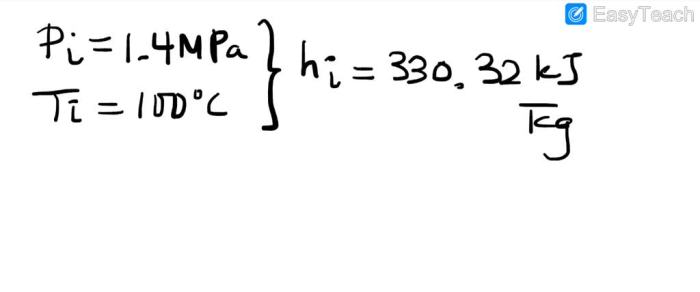
A closed rigid tank is a container designed to hold fluids under pressure without allowing any mass to enter or leave the system. It has a fixed volume, typically measured in cubic units. Closed rigid tanks play a vital role in engineering applications, particularly in fluid dynamics, thermodynamics, and process engineering.
Fluid Properties
The type of fluid contained within the tank can significantly impact its behavior. Common fluids include liquids (such as water, oil, or gasoline) and gases (such as air, nitrogen, or helium). Fluid properties such as density, viscosity, and pressure influence the tank’s performance and the processes occurring within it.
- Density:Density affects the mass and weight of the fluid, influencing the pressure distribution within the tank.
- Viscosity:Viscosity measures the fluid’s resistance to flow, affecting the rate of fluid movement and energy dissipation.
- Pressure:Pressure is the force exerted by the fluid on the tank walls, influenced by the fluid’s volume, temperature, and composition.
Thermodynamic Processes, A closed rigid tank whose volume is 1.5
Various thermodynamic processes can occur within a closed rigid tank, including:
- Isochoric process:Volume remains constant while temperature and pressure change.
- Isobaric process:Pressure remains constant while volume and temperature change.
- Isothermal process:Temperature remains constant while volume and pressure change.
- Adiabatic process:No heat is transferred in or out of the tank, resulting in changes in temperature, volume, and pressure.
These processes affect fluid properties and tank behavior, influencing applications such as energy storage and conversion.
Applications and Limitations
Closed rigid tanks find diverse applications in engineering and industry, including:
- Energy storage:Storing compressed gases or liquids for power generation or propulsion.
- Process engineering:Containing fluids in chemical reactions, fluid mixing, and separation processes.
- Aerospace:Fuel and propellant tanks in rockets and aircraft.
Advantages:
- Controlled environment:Prevents mass exchange with the surroundings, allowing for precise control of fluid properties.
- Pressure containment:Withstands high pressures, enabling storage and handling of pressurized fluids.
- Safety:Closed design minimizes leakage and potential hazards associated with fluid release.
Disadvantages:
- Limited volume:Fixed volume restricts the amount of fluid that can be stored or processed.
- Material constraints:Tank materials must withstand the pressure and chemical compatibility of the contained fluid.
- Maintenance:Regular inspections and maintenance are necessary to ensure tank integrity and safety.
FAQ Corner: A Closed Rigid Tank Whose Volume Is 1.5
What are the advantages of using closed rigid tanks?
Closed rigid tanks offer several advantages, including their ability to withstand high pressures, prevent fluid leakage, and maintain constant volume. They are also relatively easy to design and manufacture, making them a cost-effective solution for many applications.
What are the limitations of using closed rigid tanks?
Closed rigid tanks have certain limitations, such as their inability to accommodate changes in volume, which can lead to pressure fluctuations. Additionally, they can be susceptible to corrosion and other environmental factors, which may affect their integrity over time.
How do fluid properties affect the behavior of closed rigid tanks?
Fluid properties such as density, viscosity, and pressure significantly influence the behavior of closed rigid tanks. These properties affect the pressure exerted on the tank walls, the flow characteristics of the fluid, and the overall performance of the system.