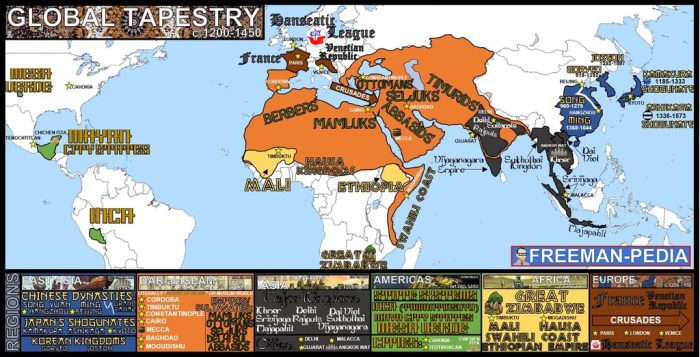
Embark on an illuminating journey through AP World History Unit 2 vocabulary, where the threads of globalization and interdependence intertwine to weave a captivating tapestry of world history. From the dawn of interconnectedness to its profound impact on societies and civilizations, this exploration promises to unravel the complexities of our globalized world.
As we delve into the intricacies of key terms, primary source analysis, and historical perspectives, we will uncover the forces that have shaped our present-day interconnectedness. Join us as we trace the evolution of globalization and interdependence, examining their causes, consequences, and enduring legacy.
Define Key Terms
Globalization and interdependence are two terms that are often used to describe the increasing interconnectedness of the world. Globalization refers to the process of increasing interaction and interdependence between people, companies, and governments worldwide. Interdependence, on the other hand, refers to the mutual reliance of different parts of a system or group on each other.
Globalization
Globalization has been driven by a number of factors, including advances in transportation and communication technology, the rise of multinational corporations, and the spread of free trade agreements. Globalization has had a profound impact on world history, leading to increased economic growth, cultural exchange, and political cooperation.
As we delve into AP World History Unit 2 vocabulary, we may encounter terms related to the concept of masking in audiology. Masking in audiology refers to the phenomenon where one sound can interfere with the perception of another, affecting our ability to hear and understand speech.
Returning to AP World History Unit 2 vocabulary, this understanding can provide insights into how external factors can influence our perceptions and shape historical narratives.
However, it has also led to increased inequality, environmental degradation, and the spread of disease.
Interdependence
Interdependence is a key aspect of globalization. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, countries and regions become more reliant on each other for goods, services, and resources. This interdependence can be both positive and negative. On the one hand, it can lead to increased cooperation and stability.
On the other hand, it can also make countries more vulnerable to economic shocks and political instability in other parts of the world.
Analyze Primary Sources
Analyzing primary sources is a crucial aspect of understanding historical events and their impact on the development of globalization and interdependence. Primary sources provide firsthand accounts, insights, and perspectives from the individuals involved in or affected by these processes.
Examining a Historical Document
To analyze a historical document, consider its:
- Author:Who wrote the document and what was their perspective?
- Date and Context:When was the document created and what were the circumstances surrounding its creation?
- Purpose:Why was the document written and what was its intended audience?
- Content:What information does the document provide and how does it relate to the topic of globalization and interdependence?
By carefully examining these aspects, you can gain a deeper understanding of the document’s significance and how it sheds light on the historical processes it describes.
Examining an Artifact
When analyzing an artifact, consider its:
- Type:What kind of artifact is it (e.g., tool, weapon, artwork)?
- Origin:Where was the artifact made and by whom?
- Date:When was the artifact created?
- Purpose:What was the artifact used for and how does it relate to the topic of globalization and interdependence?
- Condition:What is the current condition of the artifact and how does it affect its interpretation?
By examining these aspects, you can gain insights into the artifact’s significance and how it provides evidence of historical processes.
Identify Causes and Consequences
Globalization and interdependence have become increasingly prominent forces in the modern world. This interconnectedness has its roots in a complex interplay of factors, and its consequences have far-reaching implications for different regions and societies.
Factors Contributing to Globalization and Interdependence
- Advancements in transportation and communication technology have made it easier and faster to move goods, services, and people across borders.
- Economic policies, such as free trade agreements, have reduced barriers to international trade and investment.
- Political changes, including the end of the Cold War and the rise of multinational organizations, have created a more interconnected global system.
Positive Consequences of Globalization and Interdependence
- Increased economic growth and prosperity, as countries can access larger markets and benefit from specialization.
- Greater cultural exchange and understanding, as people from different regions interact and share ideas.
- Improved access to goods and services, as consumers have a wider variety of choices.
Negative Consequences of Globalization and Interdependence
- Increased economic inequality, as some countries and regions benefit more from globalization than others.
- Environmental degradation, as increased production and consumption lead to pollution and resource depletion.
- Loss of cultural identity, as local traditions and customs are influenced by global trends.
Compare Perspectives: Ap World History Unit 2 Vocab
Globalization and interdependence have profound impacts on societies worldwide, but different perspectives exist on their consequences. Historians, economists, and policymakers often have varying views on these complex phenomena.
Historians’ Perspectives, Ap world history unit 2 vocab
- Emphasize the long-term historical processes and patterns of globalization.
- Examine the cultural, social, and political consequences of globalization over time.
- Consider the role of imperialism, colonialism, and technological advancements in shaping globalization.
Economists’ Perspectives
- Focus on the economic dimensions of globalization, such as trade, investment, and financial flows.
- Analyze the impact of globalization on economic growth, inequality, and development.
- Examine the role of international organizations like the World Bank and International Monetary Fund in promoting globalization.
Policymakers’ Perspectives
- Concerned with the practical implications of globalization for their societies.
- Develop policies to manage the economic, social, and environmental challenges posed by globalization.
- Negotiate international agreements and regulations to address issues related to trade, migration, and climate change.
Create a Timeline
A timeline is a visual representation of events arranged in chronological order. It provides a clear and concise overview of key developments and their relationships over time. Creating a timeline for globalization and interdependence helps us understand the evolution of these concepts and their impact on the world.
Key Events and Developments
The timeline should include the following key events and developments:
- 1492: Christopher Columbus’s arrival in the Americas
- 1600: Establishment of the Dutch East India Company
- 1776: American Revolution
- 1800: Industrial Revolution begins in Europe
- 1869: Completion of the first transcontinental railroad in the United States
- 1870: Suez Canal opens
- 1914-1918: World War I
- 1929: Global economic depression
- 1945: United Nations is founded
- 1989: Fall of the Berlin Wall
- 1991: World Wide Web is launched
- 2001: September 11 attacks
- 2008: Global financial crisis
- 2020: COVID-19 pandemic
Each event should be accompanied by a brief description and, if possible, an image to illustrate its significance.
Organize a Table
To understand the complex phenomenon of globalization and interdependence, it’s crucial to organize key concepts, causes, and consequences in a structured manner. One effective way to do this is by creating an HTML table that provides a clear overview and facilitates easy reference.
Key Concepts
The table should include a column for key concepts related to globalization and interdependence, such as economic integration, cultural diffusion, and technological advancements.
Causes
Another column should focus on the causes of globalization and interdependence, including factors like advancements in transportation and communication, economic policies, and political initiatives.
Consequences
Finally, the table should have a column dedicated to the consequences of globalization and interdependence, such as increased global trade, economic growth, and the spread of ideas and cultures.
Provide Illustrations
To enhance our understanding of globalization and interdependence, historical images and illustrations play a crucial role in providing visual representations of their impact.
The Columbian Exchange
The Columbian Exchange refers to the exchange of plants, animals, and ideas between the Americas and Europe following Christopher Columbus’s voyages. One notable illustration depicting this exchange is a painting by Theodor de Bry from the 16th century.
The painting shows a group of Native Americans introducing maize, potatoes, and tobacco to European explorers. It highlights the introduction of new crops from the Americas to Europe, which had a profound impact on both continents.
The Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of trade routes connecting East Asia with the Middle East and Europe. A famous illustration of the Silk Road is a 13th-century Chinese painting by Li Gonglin.
The painting depicts a caravan of merchants traveling along the Silk Road, carrying goods such as silk, spices, and tea. It illustrates the vibrant exchange of goods and ideas that occurred along this important trade route.
Elaborate on Connections
Globalization and interdependence are closely intertwined with other historical concepts like imperialism, nationalism, and industrialization. These connections have shaped the modern world in profound ways.
Imperialism and Globalization
Imperialism, the domination of one country over another, has been a driving force behind globalization. European powers established colonies around the world, which led to the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. This process created a global network of trade and interconnectedness.
Nationalism and Globalization
Nationalism, the belief in the importance of one’s own nation, has also played a role in globalization. As nations emerged and sought to assert their independence, they often engaged in economic and political competition. This competition fueled global trade and the development of new technologies.
Industrialization and Globalization
Industrialization, the transition from hand-crafted production to machine-based manufacturing, has been a major factor in globalization. The Industrial Revolution in Europe led to the mass production of goods, which were then shipped around the world. This created a global market and fostered economic interdependence.
Detail Historical Events
Globalization and interdependence have profoundly impacted the course of history. Two notable events that exemplify their transformative effects are the Columbian Exchange and the Industrial Revolution.
Columbian Exchange
The Columbian Exchange, sparked by Christopher Columbus’s voyages to the Americas in the late 15th century, marked a significant turning point in global history. The exchange of plants, animals, and diseases between the Americas, Europe, and Africa had far-reaching consequences.
- Introduction of New Crops:European settlers brought crops such as wheat, rice, and sugar to the Americas, while American crops like corn, potatoes, and tomatoes were introduced to Europe and Asia, leading to a diversification of global food sources.
- Spread of Disease:European explorers carried diseases like smallpox and measles to the Americas, where they devastated indigenous populations due to a lack of immunity. Conversely, diseases such as syphilis were brought back to Europe from the Americas.
- Population Shifts:The Columbian Exchange facilitated the transatlantic slave trade, which forced millions of Africans to the Americas as a labor force, resulting in major population shifts and cultural transformations.
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, which began in Britain in the mid-18th century, was another transformative event that accelerated globalization and interdependence.
- Technological Advancements:The Industrial Revolution introduced new technologies like the steam engine, the cotton gin, and the power loom, which dramatically increased production efficiency and fueled economic growth.
- Factory System:The factory system concentrated workers in urban centers, leading to the rise of industrial cities and a shift from rural to urban living.
- Global Trade and Expansion:Industrialized nations sought raw materials and markets for their goods, leading to increased global trade and the expansion of European colonialism.
- Environmental Impact:The Industrial Revolution’s heavy reliance on fossil fuels and the use of factories had significant environmental consequences, including pollution and deforestation.
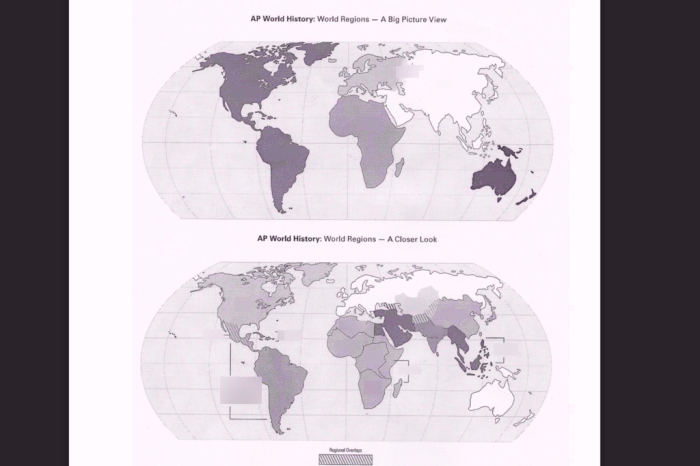
Design a Map
Maps are essential tools for understanding the spread of globalization and interdependence over time. They can help us visualize the connections between different regions and time periods, and to see how these connections have changed over time.
To create a map that shows the spread of globalization and interdependence, you can use different colors or symbols to represent different regions and time periods. For example, you could use blue to represent the spread of trade and commerce, green to represent the spread of ideas and culture, and red to represent the spread of conflict and war.
Creating a Map
To create a map, you will need to gather data on the spread of globalization and interdependence. This data can come from a variety of sources, such as historical documents, economic data, and population statistics. Once you have gathered your data, you can use a variety of software programs to create a map.
When creating a map, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The scale of the map
- The projection of the map
- The symbols and colors used on the map
The scale of the map refers to the relationship between the size of the map and the size of the area being mapped. The projection of the map refers to the way in which the three-dimensional Earth is represented on a two-dimensional map.
The symbols and colors used on the map should be clear and easy to understand.
FAQ Resource
What is the significance of globalization in world history?
Globalization has played a pivotal role in shaping world history by fostering interconnectedness, facilitating the exchange of ideas, goods, and people, and influencing cultural, economic, and political developments across the globe.
How has interdependence impacted different regions and societies?
Interdependence has had both positive and negative consequences on different regions and societies. While it has promoted economic growth and cooperation, it has also led to increased vulnerability to external shocks, economic inequality, and cultural homogenization.